Understanding Hybrid Cloud
Introduction
Definition of Hybrid Cloud
A Hybrid Cloud is a computing environment that combines the benefits of both public and private clouds by allowing data and applications to be shared between them. Hybrid Cloud provides businesses with greater flexibility, more deployment options, and helps optimize existing infrastructure, security, and compliance.
In modern IT infrastructure, Hybrid Cloud is crucial as it enables organizations to manage workloads dynamically, optimizing both performance and cost. Hybrid Cloud offers the ability to keep sensitive data secure on private clouds while leveraging the scalability of public clouds for less-sensitive data and applications.
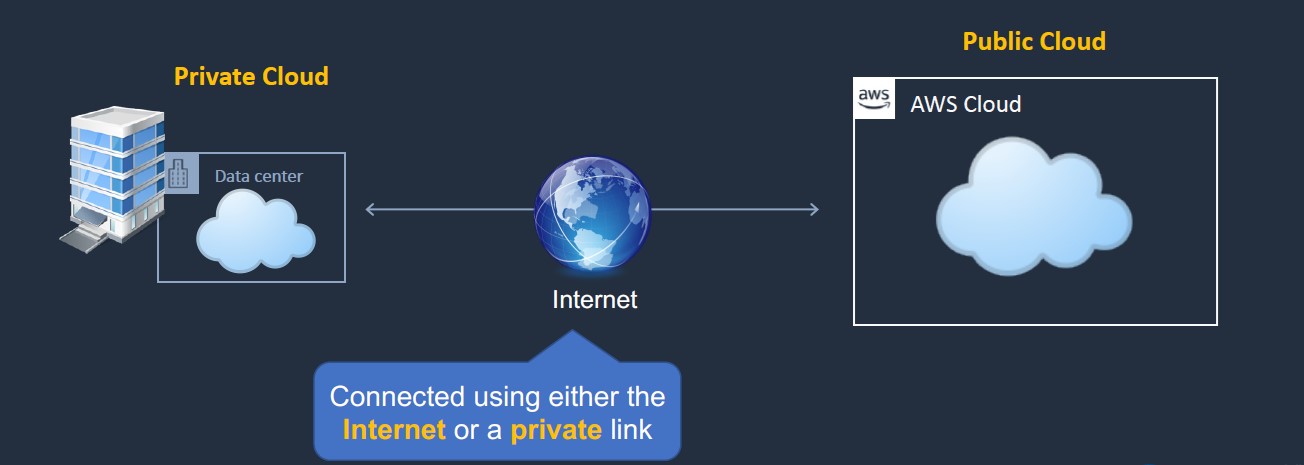
Importance of Hybrid Cloud in Business
Why Businesses Are Adopting Hybrid Cloud Solutions
Businesses are increasingly adopting Hybrid Cloud solutions to gain a competitive edge by combining the benefits of both public and private cloud environments. Hybrid Cloud provides enhanced flexibility and control over IT resources, enabling organizations to respond more quickly to changing business needs and market demands.
Key Benefits That Hybrid Cloud Offers to Enterprises
Hybrid Cloud offers several key benefits to enterprises, including:
- Increased Agility: Quickly adapt to market changes by scaling IT resources up or down as needed.
- Improved Cost Management: Optimize costs by using public clouds for non-sensitive workloads while keeping critical data secure on private clouds.
- Enhanced Security: Maintain control over sensitive data with on-premises infrastructure while leveraging cloud resources.
- Business Continuity: Ensure business continuity with robust disaster recovery and backup solutions.
Section 1: Understanding Cloud Computing
Different Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing comes in various forms, each offering distinct characteristics and benefits:
- Public Cloud: Operated by third-party providers, public clouds offer scalable resources over the internet. Examples include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Public clouds are ideal for non-sensitive applications and provide cost-effective solutions with high availability.
- Private Cloud: Dedicated to a single organization, private clouds offer greater control over data and applications. Private clouds are often hosted on-premises or in a third-party data center. Private clouds are suitable for sensitive data and applications that require stringent security and compliance.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private clouds to offer the best of both worlds. Hybrid Cloud enables seamless integration and data portability between environments, providing flexibility and control over IT resources.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides several key benefits:
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand, allowing businesses to handle fluctuations in workload efficiently.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go pricing models help optimize costs by only paying for the resources used.
- Flexibility and Agility: Quickly deploy and manage applications, enabling faster innovation and time-to-market.
Section 2: What is a Hybrid Cloud?
Components of a Hybrid Cloud
A Hybrid Cloud environment integrates both public and private clouds, enabling data and application interoperability across these platforms:
- Public Cloud Integration: Provides scalability and cost savings for non-sensitive data and applications.
- Private Cloud Integration: Ensures data privacy and compliance for sensitive information, offering greater control and security.
- Hybrid Cloud Management Platform: Facilitates seamless integration and management of both environments, ensuring consistency and performance.
How Hybrid Cloud Works
The Hybrid Cloud leverages a combination of public and private cloud resources, connected through secure networking protocols. This integration enables organizations to share data and applications between environments while maintaining control over sensitive information. Hybrid Cloud architecture provides flexibility, allowing workloads to move seamlessly between clouds based on business needs.
Hybrid Cloud vs. Other Cloud Models
Compared to other cloud models, Hybrid Cloud offers distinct advantages:
- Flexibility: Combines the benefits of public and private clouds, offering customizable solutions.
- Data Control: Ensures sensitive data remains secure on private clouds while leveraging public clouds for scalability.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrates existing IT infrastructure with cloud resources, preserving investments.
Section 3: Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
Scalability and Flexibility
The Hybrid Cloud provides scalability and flexibility by allowing businesses to allocate resources dynamically, responding to changing demands. Organizations can scale up resources during peak times and scale down when demand decreases, optimizing performance and cost.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Hybrid Cloud solutions enhance security and compliance by enabling businesses to keep sensitive data on private clouds while using public clouds for non-sensitive workloads. This approach ensures data protection and compliance with industry regulations, providing peace of mind for organizations.
Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Optimization
By leveraging the Hybrid Cloud, organizations can optimize resource allocation and reduce costs. Public clouds offer cost-effective scalability for non-sensitive applications, while private clouds ensure data security and compliance. This balance allows businesses to maximize the benefits of both environments while minimizing expenses.
Section 4: Challenges of Hybrid Cloud
Complexity of Management and Integration
Managing and integrating Hybrid Cloud environments can be complex, requiring robust tools and strategies. Organizations must ensure seamless communication and interoperability between public and private clouds while maintaining consistent performance and security.
Security Risks and Data Privacy Concerns
Security risks and data privacy concerns are significant challenges in Hybrid Cloud environments. Organizations must implement comprehensive security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulations. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments.
Network Latency and Reliability
Network latency and reliability can impact the performance of Hybrid Cloud environments. Organizations must invest in high-performance networking solutions to ensure consistent connectivity and minimize downtime. Redundancy and failover mechanisms are also essential to maintain reliable operations.
Section 5: Use Cases and Industries
Real-World Use Cases of Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud solutions are used in various industries to achieve different objectives:
- Healthcare: Enables secure storage of patient data on private clouds while using public clouds for research and analytics.
- Finance: Facilitates compliance with regulations by keeping sensitive financial data on private clouds while using public clouds for customer-facing applications.
- Manufacturing: Supports real-time data analytics by integrating IoT data from factories with cloud-based analytics platforms.
Industries Benefiting from Hybrid Cloud Solutions
Several industries benefit from Hybrid Cloud solutions, including:
- Retail: Improves customer experience with data-driven insights and personalized marketing.
- Media and Entertainment: Enables efficient content distribution and media streaming with scalable cloud resources.
- Government: Ensures data security and compliance while enabling collaboration across departments.
Section 6: Best Practices for Implementing Hybrid Cloud
Developing a Comprehensive Strategy
Organizations should develop a comprehensive Hybrid Cloud strategy that aligns with their business goals and IT requirements. This strategy should consider factors such as workload placement, data security, and integration with existing infrastructure.
Ensuring Security and Compliance
Implementing robust security and compliance measures is essential for successful Hybrid Cloud deployments. Organizations should conduct regular security assessments, implement encryption and access controls, and stay updated on industry regulations to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance.
Leveraging Automation and Monitoring
Automation and monitoring tools can enhance the efficiency and reliability of Hybrid Cloud environments. Organizations should leverage automation to streamline processes, improve resource allocation, and reduce manual errors. Monitoring solutions provide real-time insights into performance, enabling proactive management and troubleshooting.
Continuous Evaluation and Optimization
Continuous evaluation and optimization of Hybrid Cloud environments are crucial for maximizing benefits. Organizations should regularly assess their cloud strategy, monitor performance metrics, and identify areas for improvement. This iterative approach ensures that the Hybrid Cloud solution remains aligned with business objectives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Hybrid Cloud offers a powerful solution for businesses seeking to optimize their IT resources and achieve greater flexibility. By combining the benefits of public and private clouds, organizations can enhance agility, improve security, and optimize costs. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, robust security measures, and continuous optimization.
As the cloud computing landscape continues to evolve, Hybrid Cloud solutions will play a vital role in helping businesses navigate the complexities of modern IT environments and drive innovation.
Related content