Software as a Service (SaaS)
Introduction
Software as a Service (SaaS) represents a significant shift in how software applications are delivered and consumed. Unlike traditional software that requires installation on individual devices, SaaS provides applications over the internet, offering users the ability to access software from anywhere with an internet connection. This model simplifies the deployment and management of software, making it a popular choice for businesses and individual users alike.
What is Software as a Service (SaaS)?
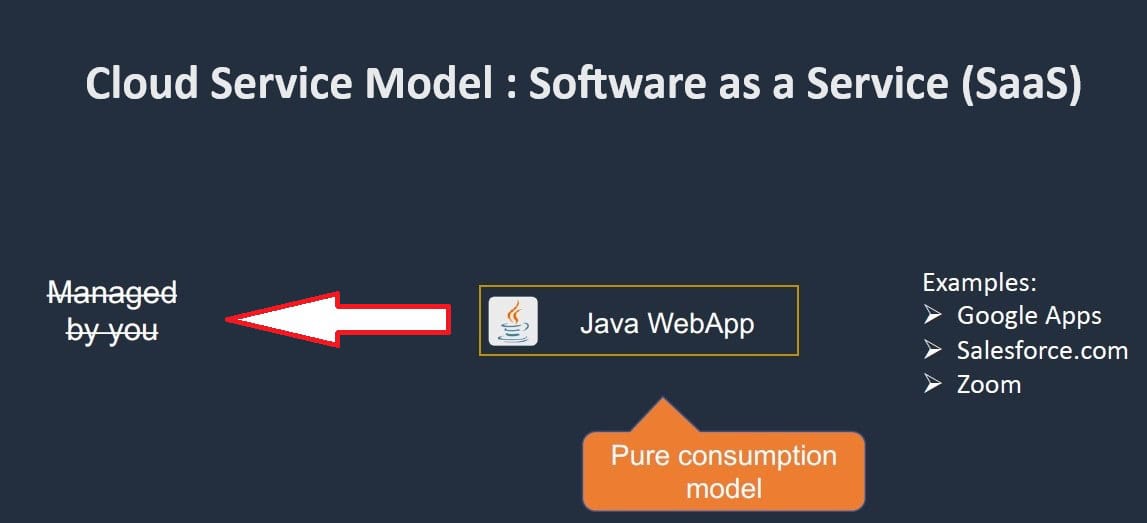
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing model where software applications are hosted and managed by a third-party provider and delivered to users over the internet. Instead of purchasing and installing software on local devices, users subscribe to the software on a recurring basis, typically through a web browser. SaaS eliminates the need for internal IT infrastructure and maintenance, as the provider handles all aspects of software management.
Benefits of Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS offers a range of advantages for both businesses and individual users:
- Cost Efficiency: SaaS eliminates the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and software, as costs are typically based on a subscription model.
- Accessibility: Users can access SaaS applications from any location with an internet connection, providing flexibility and convenience.
- Automatic Updates: SaaS providers handle software updates and patches, ensuring users always have access to the latest features and security improvements.
- Scalability: SaaS solutions can easily scale to accommodate growing user demands, allowing businesses to adjust their subscriptions as needed.
- Reduced IT Burden: With the provider managing software maintenance and infrastructure, internal IT teams can focus on other critical tasks.
Shared Responsibility Model for Software as a Service (SaaS)
The Shared Responsibility Model for SaaS outlines the division of responsibilities between the SaaS provider and the user. This model is essential for understanding who is accountable for various aspects of the software and its usage.
Responsibilities of the SaaS Provider:
- Application Management: The provider is responsible for managing and maintaining the software application, including updates, bug fixes, and feature enhancements.
- Infrastructure Management: The provider handles the underlying infrastructure, including servers, storage, and network resources.
- Security: The provider ensures the security of the application and infrastructure, including data protection and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Availability: The provider guarantees the availability and performance of the application, ensuring reliable access and uptime.
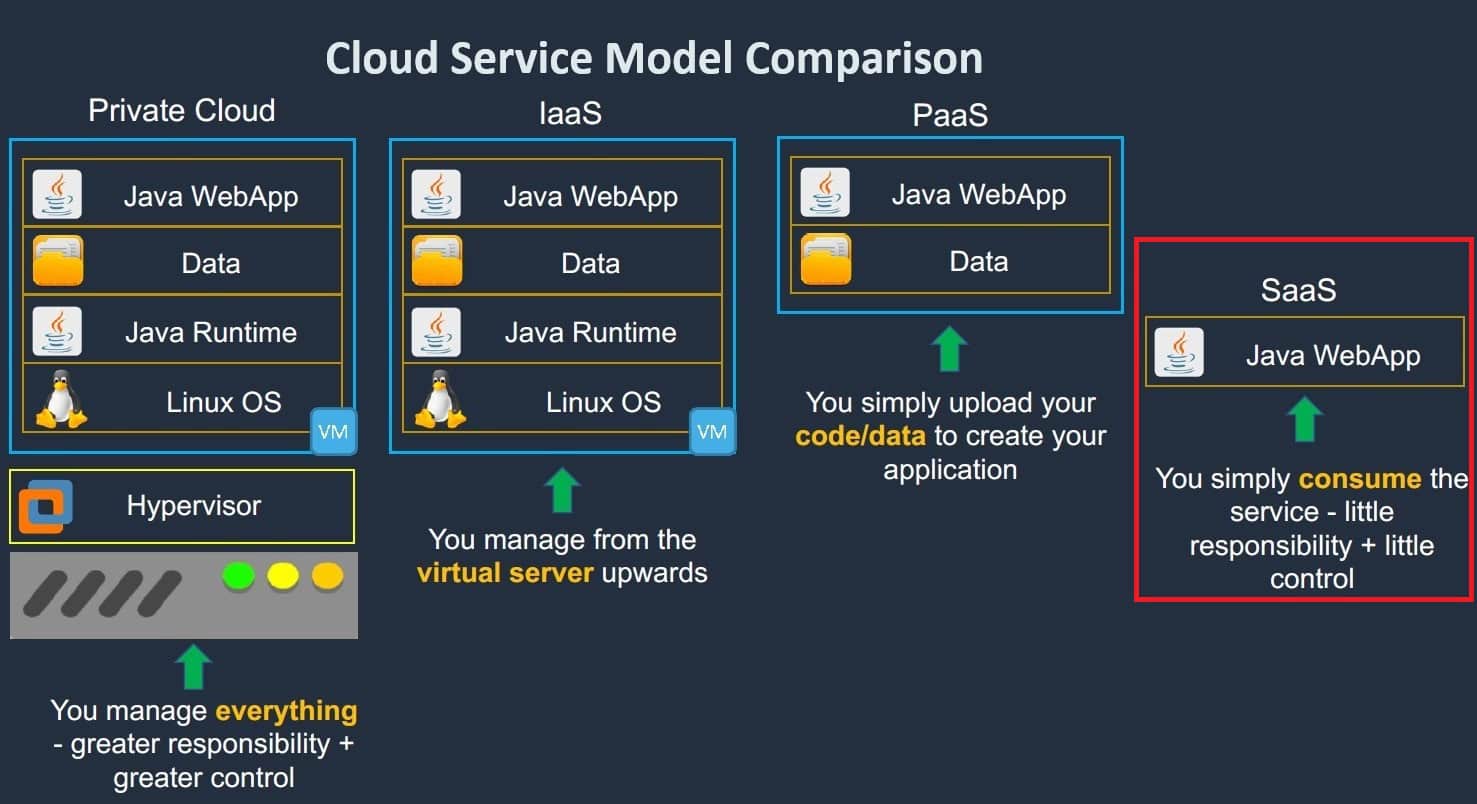
Responsibilities of the User:
- Application Usage: Users are responsible for how they use the application, including adherence to licensing agreements and acceptable use policies.
- Data Management: Users must manage their own data within the application, including data entry, storage, and backup.
- User Access Management: Users are responsible for managing access permissions and ensuring secure login practices for their accounts.
- Compliance: Users must ensure their use of the application complies with relevant laws and regulations, including data privacy and security standards.
Where does the Sofware as a service(Saas) stand?
Common Use Cases of Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is applicable in various scenarios, including:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): SaaS CRM platforms help businesses manage customer interactions, sales, and support.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): SaaS ERP systems provide integrated management of core business processes, such as finance, HR, and supply chain.
- Collaboration Tools: SaaS applications like email, chat, and project management tools enhance team collaboration and communication.
- Accounting and Finance: SaaS accounting software simplifies financial management, invoicing, and reporting.
- Human Resources (HR): SaaS HR platforms streamline employee management, payroll, and recruitment processes.
Common Providers of Software as a Service (SaaS)
Several leading SaaS providers offer a wide range of applications and services:
- Salesforce: A leading CRM platform that provides a comprehensive suite of tools for managing customer relationships and sales processes.
- Microsoft 365: Offers a range of productivity tools, including Word, Excel, and Outlook, delivered as SaaS.
- Google Workspace: Provides cloud-based applications for collaboration, including Gmail, Google Drive, and Google Docs.
- Slack: A popular communication and collaboration platform that facilitates team messaging and project management.
- Zoom: A widely used video conferencing and webinar platform, offering scalable and reliable communication solutions.
- QuickBooks Online: A SaaS accounting solution for managing finances, invoicing, and payroll.
Examples of Software as a Service (SaaS)
Here are some practical examples of SaaS applications:
- Salesforce: Used for managing customer relationships, sales processes, and marketing campaigns.
- Google Workspace: A suite of productivity tools including email, document creation, and cloud storage.
- Slack: Provides team communication and collaboration features, including channels, direct messages, and file sharing.
- Zoom: Facilitates online meetings, webinars, and video conferences with features for screen sharing and recording.
- QuickBooks Online: Offers accounting and financial management tools for businesses, including invoicing and expense tracking.
Conclusion
Software as a Service (SaaS) represents a transformative approach to software delivery, making it easier for businesses and individuals to access and manage applications without the complexities of traditional software installations. The benefits of SaaS, including cost efficiency, accessibility, and automatic updates, make it an attractive option for many users. With a diverse range of SaaS providers such as Salesforce, Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Slack, and Zoom, there are solutions available to meet various needs and preferences.
As technology continues to evolve, SaaS will remain a pivotal element in the cloud computing landscape, offering flexible, scalable, and cost-effective software solutions that drive innovation and productivity. Embracing SaaS can help organizations streamline their operations and stay competitive in an increasingly digital world.
Related content