Understanding Private Cloud
Introduction
The Private Cloud is a cloud computing model where all the cloud resources are exclusively used by a single organization. Unlike Public Clouds, which share resources among multiple users, the Private Cloud ensures that all the computing power, storage, and networking capabilities are dedicated solely to one entity. This makes it an ideal choice for organizations that need higher levels of security, control, and compliance, while still enjoying the flexibility and efficiency of cloud computing.
What is a Private Cloud?
A Private Cloud is a bespoke cloud computing environment tailored specifically for one organization. It can be hosted on-premises within the organization's own facilities or managed externally by a third-party provider. Private Clouds offer many of the same benefits as Public Clouds, such as scalability and flexibility, but come with additional security and control features designed to meet the specific needs of the organization. Technologies like virtualization and containerization are commonly employed to implement and manage Private Clouds, ensuring they deliver robust and reliable performance.
Benefits of Private Cloud
Private Clouds provide several key advantages that make them an attractive option for many businesses:
- Enhanced Security: Since the Private Cloud is not shared with other organizations, it provides superior security measures and compliance controls, ideal for handling sensitive data and meeting regulatory standards.
- Greater Control: Organizations gain complete control over their cloud infrastructure, including hardware, network setups, and software environments, allowing for a highly customized IT environment.
- Customization: Private Clouds can be configured to meet specific business requirements, offering customized setups and integrations with existing IT systems for enhanced flexibility.
- Performance: With dedicated resources, Private Clouds often deliver better performance and reliability compared to Public Clouds, which is particularly beneficial for high-demand applications and critical workloads.
- Compliance: Private Clouds facilitate meeting rigorous compliance requirements by providing dedicated, controlled environments that are easier to monitor and manage for regulatory adherence.
Shared Responsibility Model
The Shared Responsibility Model outlines how responsibilities are divided between the Private Cloud provider and the organization using the Private Cloud. Here’s a breakdown of these responsibilities:
Responsibilities of the Provider:
- Infrastructure Management: The provider takes care of physical hardware, network infrastructure, and the operations of the data center where the Private Cloud is hosted.
- Hardware Security: The provider ensures the security of physical hardware and the underlying infrastructure to prevent unauthorized access and breaches.
- Software Updates: The provider may be responsible for updates and patches for any underlying software or management tools included in the Private Cloud environment.
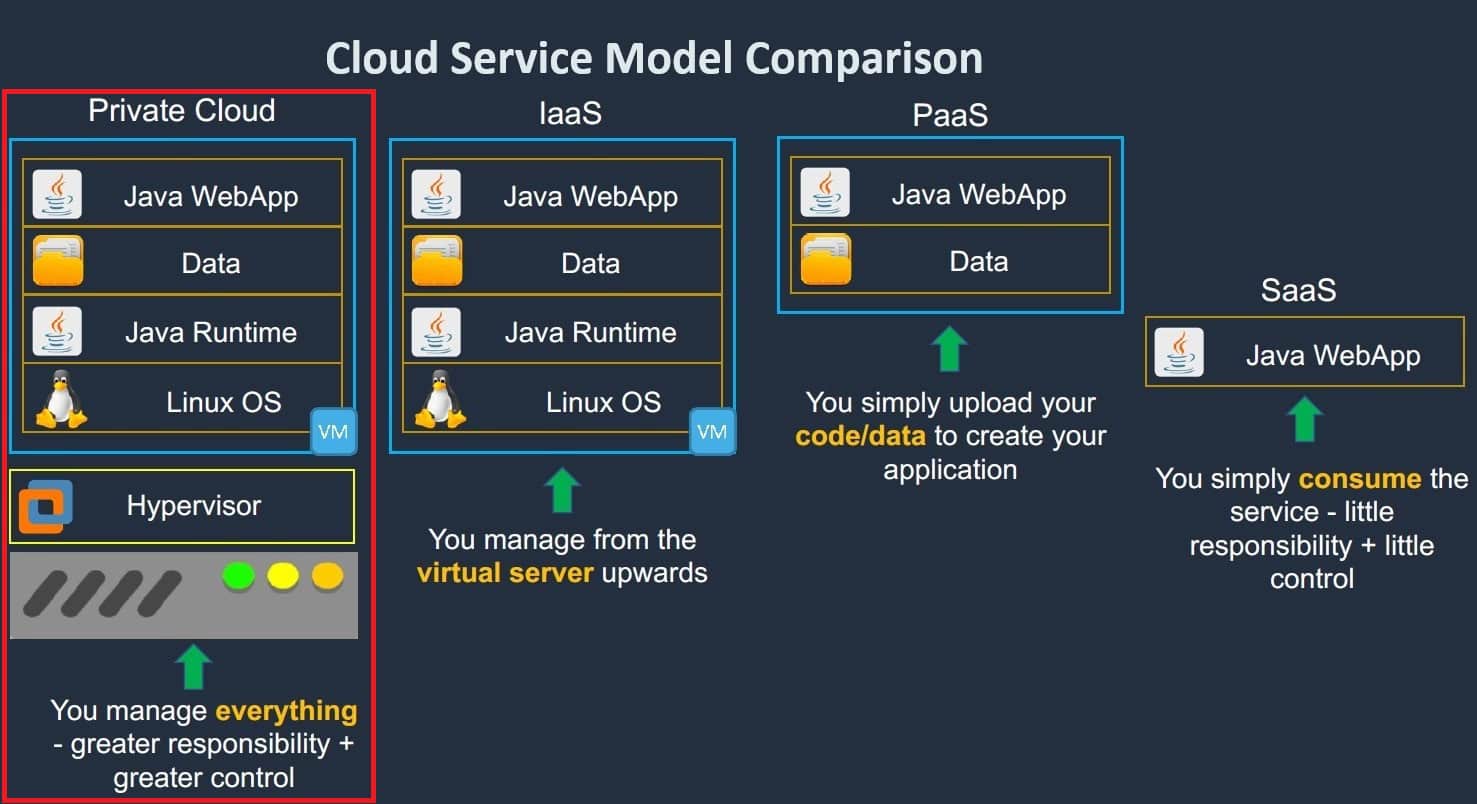
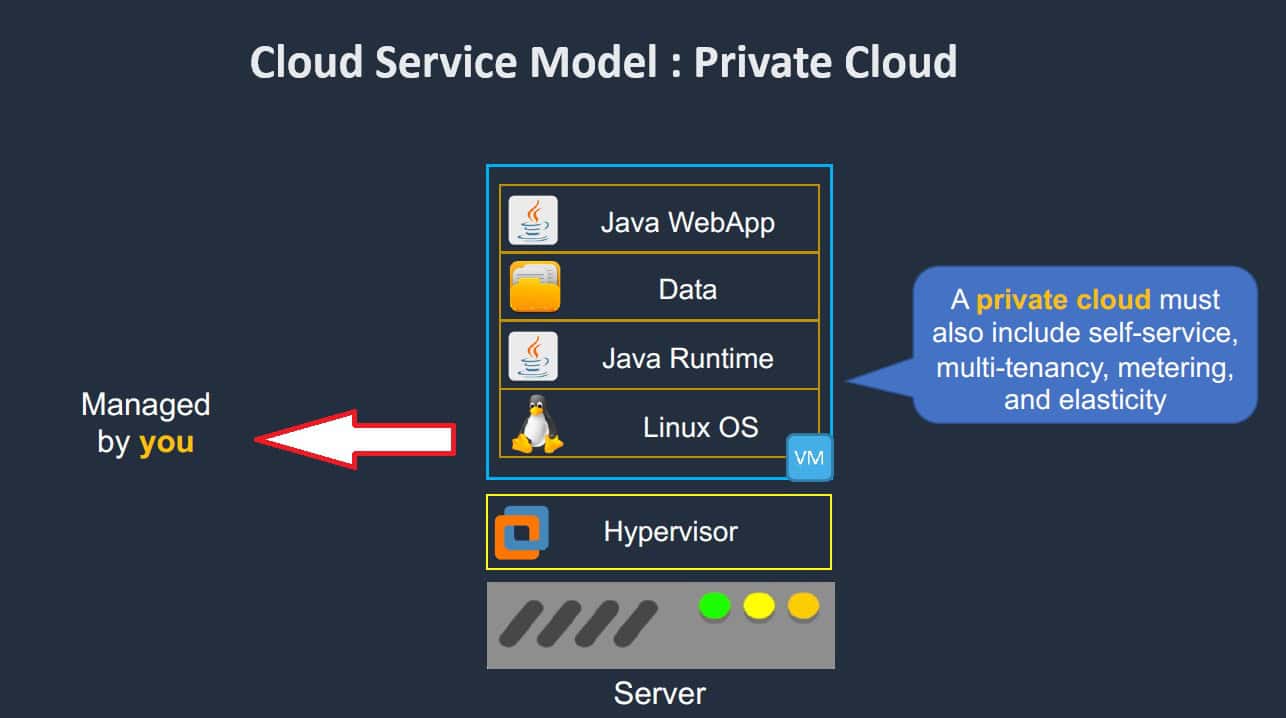
Responsibilities of the User:
- Application Management: The organization is responsible for managing its own applications, including their installation, configuration, and updates to ensure optimal performance.
- Data Security: The organization must handle data security, including encryption, backups, and access controls, to protect sensitive information from potential threats.
- Network Security: The organization is tasked with configuring and managing firewalls, virtual networks, and other security measures within the Private Cloud environment.
- Compliance: The organization is responsible for ensuring that its operations within the Private Cloud meet regulatory and industry compliance standards.
The clear division of responsibilities in the Shared Responsibility Model helps maintain a secure and compliant Private Cloud environment.
Common Use Cases
Private Clouds are versatile and serve a range of business needs:
- Regulated Industries: Sectors like healthcare, finance, and government that require high levels of data security and compliance often use Private Clouds to meet stringent regulatory standards.
- Large Enterprises: Large organizations with complex IT infrastructure and substantial data requirements benefit from the scalability and customization that Private Clouds offer.
- Hybrid Cloud Environments: Many businesses use Private Clouds alongside Public Clouds to create hybrid cloud solutions that leverage the strengths of both models, optimizing flexibility and efficiency.
- High-Performance Computing: Businesses needing intensive computational power, such as research institutions and data analytics firms, use Private Clouds to manage and process large-scale workloads.
- Legacy System Integration: Private Clouds assist in integrating legacy systems with modern cloud applications, making it easier to transition and enhance functionality without disrupting existing operations.
Leading Private Cloud Providers
Several top-tier providers offer comprehensive Private Cloud solutions to cater to diverse business requirements:
- VMware: VMware specializes in virtualization and cloud management, providing a suite of tools for deploying and managing Private Cloud environments effectively.
- Microsoft Azure Stack: Azure Stack extends Microsoft Azure’s cloud capabilities to Private Clouds, offering a hybrid cloud experience with seamless integration into Azure services.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Outposts: AWS Outposts deliver AWS cloud infrastructure and services to on-premises locations, creating a cohesive Private Cloud experience with AWS management capabilities.
- IBM Cloud Private: IBM Cloud Private focuses on containerization and enterprise-grade applications, offering a suite of solutions for building and managing Private Clouds.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Dedicated Region: OCI provides dedicated regions for Private Clouds, offering high performance and security for mission-critical workloads.
Examples of Private Cloud
Here are practical examples of Private Cloud implementations from leading providers:
- VMware Private Cloud: VMware’s Private Cloud solutions leverage advanced virtualization and management tools, enabling businesses to set up and operate their own Private Clouds.
- Microsoft Azure Stack: Azure Stack enables organizations to run Azure-consistent applications in their Private Clouds, extending Azure’s capabilities to on-premises environments.
- IBM Cloud Private: IBM Cloud Private offers various services and tools for building and managing Private Cloud environments, with a focus on enterprise applications and containerization.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Outposts: AWS Outposts bring AWS cloud capabilities to on-premises locations, providing a Private Cloud experience with AWS management features.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Dedicated Region: OCI Dedicated Regions deliver high-performance and secure Private Cloud environments tailored for critical business applications.
Emerging Trends in Private Cloud
Private Cloud technology is continuously evolving. Some emerging trends include:
- Integration with Edge Computing: Private Clouds are increasingly integrating with edge computing to enhance performance and support real-time data processing closer to where data is generated.
- Enhanced Security Features: As cybersecurity threats become more sophisticated, Private Cloud providers are implementing advanced security measures such as AI-driven threat detection and automated compliance management.
- Multi-Cloud Strategies: Organizations are adopting multi-cloud strategies, using Private Clouds in conjunction with multiple Public Clouds to optimize their IT infrastructure and avoid vendor lock-in.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Management Tools: New tools are emerging to simplify the management of hybrid and multi-cloud environments, offering unified visibility and control across different cloud platforms.
- Containerization and Kubernetes: Private Clouds are increasingly using containerization and Kubernetes to improve application deployment, scalability, and management.
Best Practices for Private Cloud Deployment
To ensure a successful Private Cloud deployment, consider the following best practices:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly outline the goals and requirements for your Private Cloud deployment to ensure it meets your organization’s needs and compliance standards.
- Invest in Training: Ensure your team is well-trained in Private Cloud technologies and best practices to effectively manage and optimize your cloud environment.
- Implement Robust Security Measures: Apply advanced security protocols, including encryption, access controls, and regular audits, to protect your Private Cloud from potential threats.
- Monitor and Optimize Performance: Regularly monitor your Private Cloud’s performance and make adjustments as needed to maintain optimal operation and efficiency.
- Plan for Scalability: Design your Private Cloud infrastructure with scalability in mind to accommodate future growth and evolving business needs.
Conclusion
Private Clouds offer a tailored and secure cloud computing model, providing organizations with exclusive access to cloud resources. They deliver enhanced security, control, and performance, making them suitable for regulated industries, large enterprises, and high-performance computing needs. Leading providers such as VMware, Microsoft Azure Stack, AWS Outposts, IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offer robust Private Cloud solutions to meet varied business requirements.
As the cloud computing landscape continues to evolve, Private Clouds remain essential for organizations seeking solutions that align with their specific needs and compliance standards. By leveraging Private Cloud environments, businesses can retain control over their IT infrastructure while benefiting from the flexibility and efficiency of modern cloud technology.
Related content