Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Introduction
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) represents a pivotal model in cloud computing that offers virtualized computing resources over the internet. Unlike traditional IT infrastructure, IaaS provides a scalable and flexible solution for accessing computing power, storage, and networking capabilities without the need to invest in physical hardware. This model is particularly beneficial for businesses that need to scale their infrastructure rapidly and efficiently.
What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. In this model, users rent IT infrastructure components such as servers, storage, and networking from a cloud service provider rather than owning and managing physical hardware. IaaS enables organizations to deploy and manage their applications, operating systems, and data on a scalable infrastructure without the complexity of maintaining physical servers.
Benefits of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
The IaaS model offers numerous advantages for businesses and individual users:
- Cost Efficiency: IaaS reduces the need for capital investment in physical hardware, as users pay for resources on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Scalability: IaaS allows for the rapid scaling of resources up or down based on demand, providing flexibility and cost control.
- Accessibility: Users can access IaaS resources from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration.
- Disaster Recovery: IaaS providers typically offer built-in disaster recovery and backup solutions, enhancing data protection and availability.
- Reduced Maintenance: The cloud provider manages hardware maintenance, reducing the burden on internal IT teams and allowing them to focus on other tasks.
Shared Responsibility Model
The Shared Responsibility Model in IaaS defines the division of responsibilities between the cloud service provider and the user. Here’s how it typically works:
Responsibilities of the Provider:
- Infrastructure Management: The provider is responsible for managing the physical data centers, servers, storage, and network resources.
- Virtualization Layer: The provider manages the virtualization layer that enables the creation of virtual machines and other resources.
- Security: The provider ensures the security of the infrastructure, including physical security and network security measures.
- Availability: The provider guarantees the availability and uptime of the infrastructure services, including maintenance and updates.
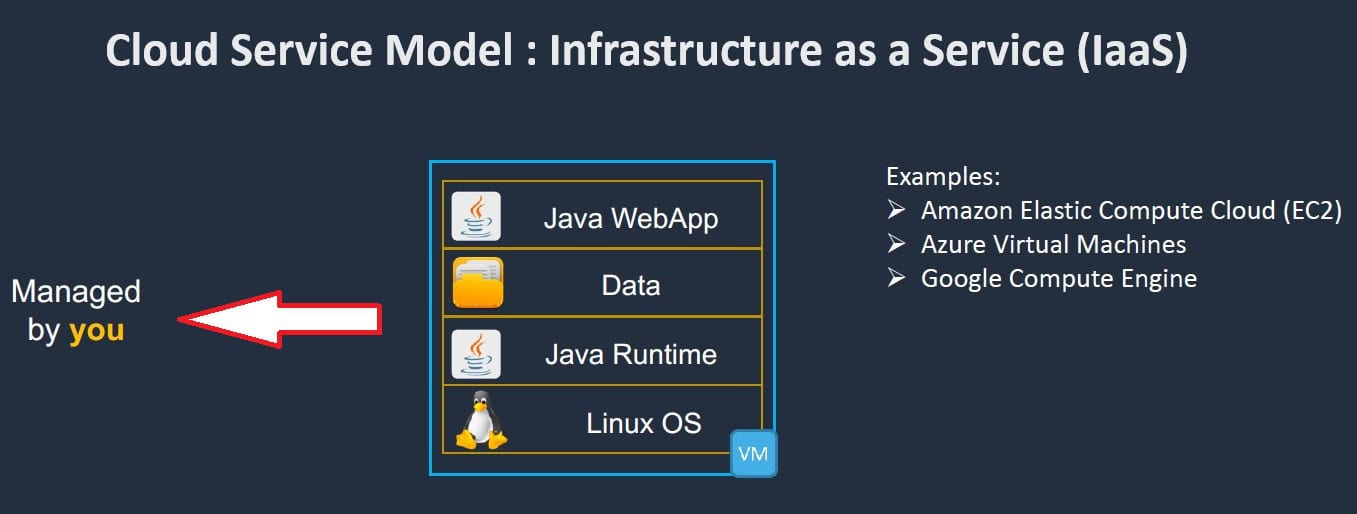
Responsibilities of the User:
- Application Management: Users are responsible for managing their own applications, including installation, configuration, and updates.
- Data Management: Users must manage their own data, including data storage, backup, and security.
- Operating System: Users are responsible for managing the operating systems running on their virtual machines, including updates and security patches.
- Network Security: Users must configure and manage their own firewalls, virtual networks, and security settings to protect their applications and data.
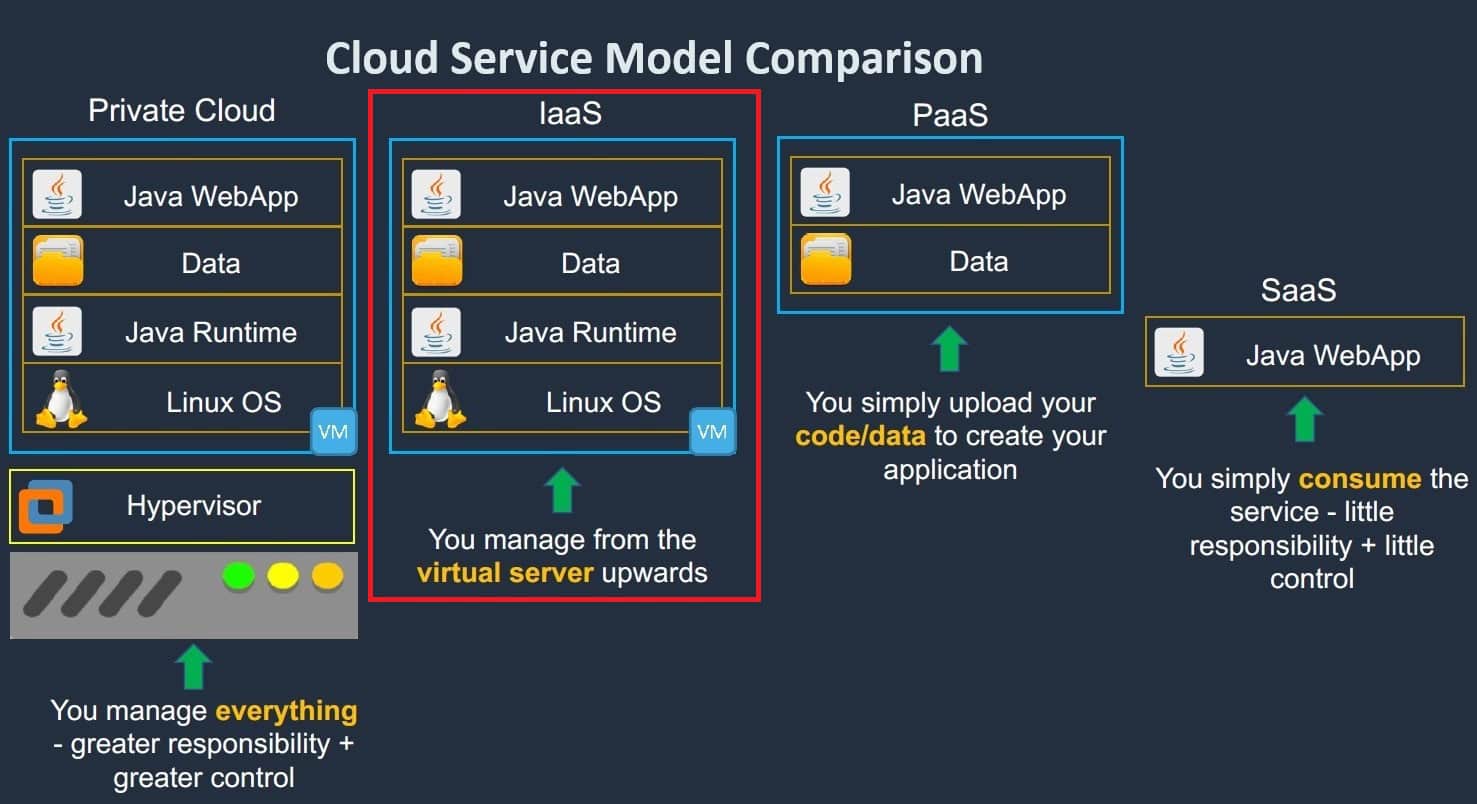
Where does the Infrastructure as a service(Iaas) stand?
Common Use Cases of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is suitable for a variety of applications and scenarios:
- Development and Testing: Developers use IaaS to create and test applications in scalable environments without investing in physical servers.
- Data Storage: Businesses utilize IaaS for scalable and secure data storage solutions, accommodating growing data needs.
- Web Hosting: IaaS provides the infrastructure needed to host websites and web applications, ensuring reliable performance and uptime.
- Backup and Recovery: IaaS offers backup and disaster recovery solutions to protect against data loss and ensure business continuity.
- Enterprise Applications: Organizations deploy and manage enterprise applications on IaaS platforms, benefiting from flexible and scalable infrastructure.
Common Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Providers
Several leading IaaS providers offer robust solutions for various needs:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is a major player in the IaaS market, providing a wide range of cloud computing services, including computing power, storage, and networking.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure offers scalable IaaS solutions with integrated services for computing, storage, and networking, as well as support for hybrid cloud environments.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP provides a comprehensive set of IaaS services, including virtual machines, storage, and networking, with a focus on high performance and scalability.
- IBM Cloud: IBM Cloud offers IaaS solutions with advanced capabilities for computing, storage, and networking, as well as integration with IBM’s other cloud services.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI): OCI provides a range of IaaS services with a focus on enterprise-grade performance, security, and scalability.
Examples of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Here are some practical examples of IaaS applications:
- Amazon EC2: A service from AWS that provides scalable virtual servers in the cloud, allowing users to run applications and workloads.
- Azure Virtual Machines: Offers scalable virtual machines on Microsoft Azure, enabling users to deploy and manage applications and services.
- Google Compute Engine: Provides virtual machines on Google Cloud Platform, designed for high-performance and scalable computing needs.
- IBM Virtual Servers: Delivers flexible virtual servers on IBM Cloud, with a focus on enterprise-grade performance and security.
- Oracle Compute: Offers scalable virtual machines and computing resources on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, with a focus on high performance and security.
Conclusion
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers a versatile and cost-effective solution for accessing and managing IT infrastructure without the need for physical hardware. With its benefits of scalability, flexibility, and reduced maintenance, IaaS is an attractive option for businesses seeking to streamline their operations and reduce costs. Leading IaaS providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offer robust solutions tailored to diverse needs.
As cloud computing continues to evolve, IaaS will remain a crucial component, providing organizations with the infrastructure they need to support their digital transformation efforts. By leveraging IaaS, businesses can focus on innovation and growth while leaving the complexities of hardware management to their cloud service provider.
Related content